UndoManager
Introduction
The UndoManager API allows web applications to modify the platform undo stack, and scope undo stacks to elements.
Motivation
Many rich text editors on the web either implement custom editing operations which are not natively supported, or create fully customized editing experiences by intercepting user interaction in hidden editable elements and applying changes to the document using DOM APIs. There are many commonly used examples of this technique, including Google Docs, CodeMirror, and the Monaco editor. Furthermore, other web applications may allow the user to undo and redo changes in a context that is completely unrelated to editing (for instance, a drawing application that allows the user to undo or redo pen strokes). All the above scenarios share a common challenge: implementing a custom undo and redo experience, often by intercepting user events that are commonly associated with undoing or redoing in the current platform (such as control-Z or command-Z).
This imposes added complexity on the web application by requiring it to store a custom undo stack (which may additionally need to be kept in sync with the platform’s undo stack). Worse yet, this makes it impossible to maintain compatibility with platform affordances for triggering undo and redo. Examples of this include the system menu bar on macOS[1], and system-wide gestures on iOS[2, 3].
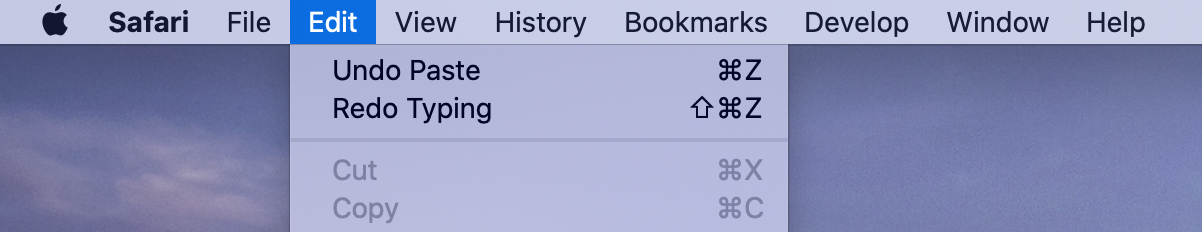
Figure 1: Undo and redo via the system menu bar on macOS.
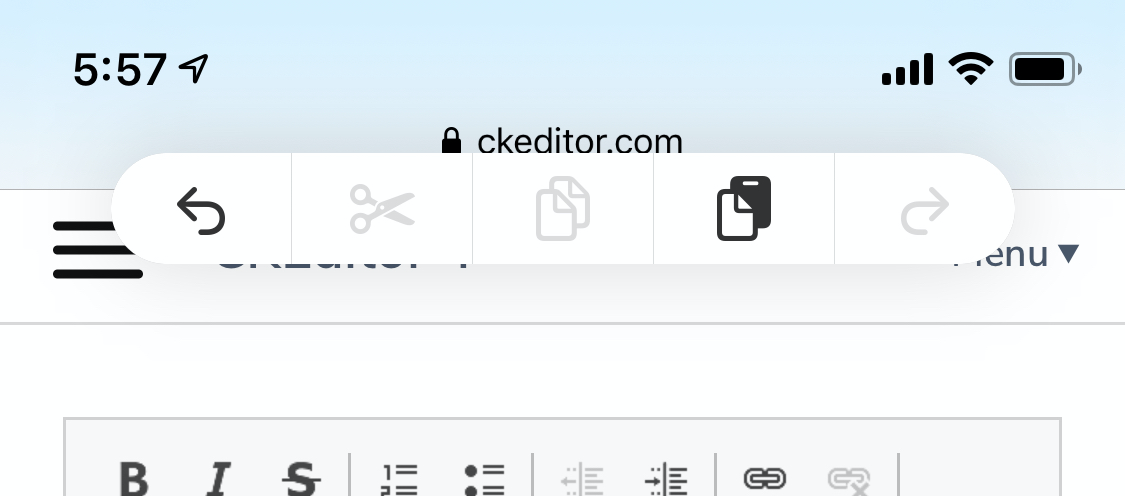
Figure 2: System-wide editing controls on iOS, shown after a three-finger tap.
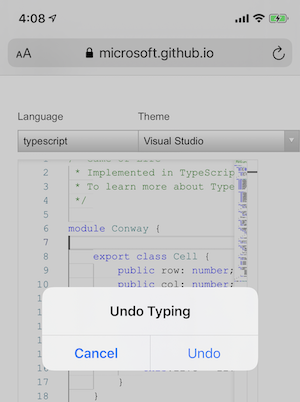
Figure 3: Modal undo UI on iOS, after shaking the device.
To address these issues, we propose an API to allow web applications to add undoable and redoable actions — represented using UndoItem — to the native undo stack, which is represented using UndoManager.
Interfaces
UndoItem
An UndoItem represents a single undoable or redoable action. A custom UndoItem is created using:
- a
label, which determines the text that is shown in system undo UI to describe the action being undone or redone. - an optional
undocallback, which is invoked when the platform undo manager pops a custom item off of the stack. - an optional
redocallback, which is invoked when the platform undo manager pushes a custom item (that has been popped) back onto the stack. - an optional
mergedflag; iftrue, this means that the undo item will be undone or redone together with the previous item in the undo stack. By default, anUndoItemis not merged.
[
Exposed=Window,
Constructor(UndoItemInit initDict)
] interface UndoItem {
readonly attribute DOMString label;
readonly attribute boolean merged;
};
callback UndoItemCallback = void ();
dictionary UndoItemInit {
required DOMString label;
UndoItemCallback undo;
UndoItemCallback redo;
boolean merged = false;
};
UndoManager
An UndoManager exposes the ability to query and manipulate the undo stack. UndoManager is backed by a list of UndoItems where each UndoItemrepresents a reversible action, such as inserting or deleting text. Items may be pushed onto the undo manager by the user agent (for instance, when typing in a text field), and they may also be added by the page using addItem.
The nth UndoItem in the stack can be queried using item(n), and the index of the current item is given by position. The length attribute exposes the total number of undo items in the stack. The undo and redo methods of UndoManager respectively decrement and increment the position, and, in the process, invoke and undo or redo methods of the previous item.
[
Exposed=Window
] interface UndoManager {
void undo();
void redo();
void addItem(UndoItem item);
UndoItem item(unsigned long index);
readonly attribute unsigned long length;
readonly attribute unsigned long position;
};
Extensions to Element
An element’s undoManager is the UndoManager associated with that element, or null if there is none (for instance, if the element is disconnected). An element also has a boolean undoScope attribute, which is initially false. If changed to true, that element and its descendants are associated with a new UndoManager, with its own undo stack.
partial interface Element {
readonly attribute UndoManager undoManager;
[CEReactions] attribute boolean undoScope;
};
Examples
Content Insertion
The following example implements a helper function, insertContentAtSelection, that takes an array of DOM nodes to insert at the current selection, as well as an optional undo label. This method replaces the selection with this content in a way that is reversible (undoable and redoable) using the platform’s undo stack.
replaceWithContent and rangeFromContent are separate helper methods that respectively (1) replace a given range with a list of DOM nodes, and (2) compute a DOMRange given a list of sibling nodes. These are both utilized in the implementation of insertContentAtSelection.
function replaceWithContent(rangeToReplace, content) {
// Returns the content being replaced.
const replacedContent = rangeToReplace.cloneContents();
rangeToReplace.deleteContents();
for (let index = content.length - 1; index >= 0; index--)
rangeToReplace.insertNode(content[index]);
return Array.from(replacedContent.childNodes);
}
function rangeFromContent(content) {
// Assumes that content is a list of DOM nodes in order.
const range = document.createRange();
range.setStartBefore(content[0]);
range.setEndAfter(content[content.length - 1]);
return range;
}
First, insertContentAtSelection uses replaceWithContent to remove the contents of the existing selection and replace it with contentToInsert; the existing content is kept in originalContent. The method then uses the browsing context’s UndoManager to add a new UndoItem. The undo and redo callbacks are, respectively, implemented by swapping out the given content to insert for the original content that was replaced, and vice versa. After undoing or redoing, it additionally selects the inserted content (if any).
function insertContentAtSelection(contentToInsert, undoLabel) {
const originalRange = getSelection().getRangeAt(0);
const originalContent = replaceWithContent(originalRange, contentToInsert);
document.undoManager.addItem(new UndoItem({
label: undoLabel || "Editing",
undo: () => {
const rangeToUndo = rangeFromContent(contentToInsert);
replaceWithContent(rangeToUndo, originalContent);
getSelection().removeAllRanges();
getSelection().addRange(rangeFromContent(originalContent) || originalRange);
},
redo: () => {
const rangeToRedo = rangeFromContent(originalContent) || originalRange;
replaceWithContent(rangeToRedo, contentToInsert);
getSelection().removeAllRanges();
getSelection().addRange(rangeFromContent(contentToInsert));
}
}));
}